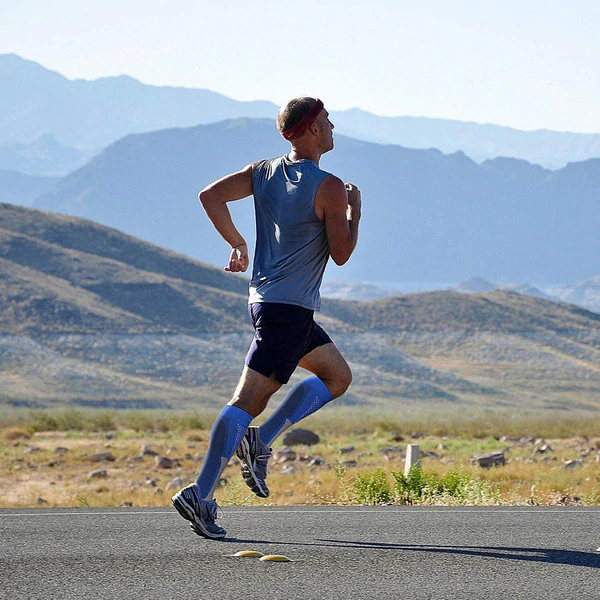
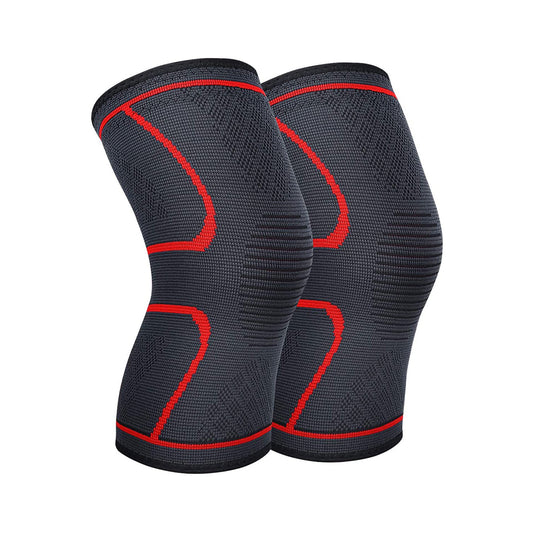
Compression stockings during or after exercise
Share
Based on our results, we recommend that athletes wear compression tights to speed up recovery, especially after significant eccentricity after vigorous exercise. Compression stockings are special garments that apply mechanical pressure to the lower leg to help stabilize, support, and compress tissue. Compression therapy began in the mid-15th century as a treatment for varicose veins.
Compression garments have been used by elite athletes for training since the late 1980s, as they enhance and accelerate recovery and improve performance in long-distance endurance events such as marathon running and road cycling.
How do compression socks work? What do they do?

When is the best time to wear compression socks during or after exercise?
Most of the benefits come after a workout, but by wearing the compression during activity, you'll start the recovery process quickly.
- Compression socks and athletes
- faster recovery
- Increase range of motion (> flexibility)
- Blood flows back to the heart and lungs faster
- Provides more oxygen to the leg muscles
- Metabolic waste from training is filtered faster (more efficient recovery)
- Counteract stasis and hypercoagulability (reduce blood clotting, important for older athletes during endurance training)
Compression stockings when exercising
How many runners wear compression socks?
The main benefit of wearing graduated compression socks (CS) is that they speed up recovery.
Wearing a CS while exercising or engaging in sports generally does not improve performance, but there are a few exceptions. However, it should be clearly stated that the main benefit of compression socks is faster recovery, whether you wear them during or after training.
Our current findings suggest that runners may slightly improve variables associated with endurance performance (i.e. time to failure) by wearing a compression garment.
For endurance-based sports, such as long-distance running and cycling, wearing compression socks during activities can result in a slight increase in performance. However, the main benefit will be seen over the next few days as you will have less muscle pain/soreness and better flexibility.
When running or cycling long distances, especially in hilly terrain, your muscles experience microtrauma and inflammation. Your jogging mechanism becomes more sloppy when you continue to run while tired. Running in compression socks increases your muscle temperature and reduces muscle pain and muscle damage, thereby reducing inflammation. This will result in a slight performance boost, but more importantly, it will speed up the post-activity recovery process.
Wearing compression socks while running has been shown to improve running efficiency and mechanics, which equates to good stride and consistent foot impact throughout.
It is also beneficial to wear CS during high-intensity interval training (HIIT) style workouts such as CrossFit, spin classes, or sports such as tennis and basketball. There's good reason Vince Carter, Allen Iverson and Kobe Bryant all wore compression tights before then-NBA Commissioner David Stern banned the use of functional clothing in games. For example, basketball is a HIIT-style activity with intermittent strength movements such as jumping and frequent acceleration and deceleration during normal play. This can lead to severe muscle damage and muscle soreness that can lead to poor shooting and game performance in back-to-back games, especially on the road.
Compression stockings after exercise
In fact, post-workout compression garments have been shown to help with recovery from muscle fatigue.
The vast majority of research into compression socks and exercise looks at compression socks after exercise. Compression socks don't affect performance and in some cases provide a slight boost. All strenuous physical activity and exercise routines will aid recovery and reduce pain by wearing graded compression socks after activity.
What is intense?
If you're sore or tired from exercise, especially in the next few days, then it's intense enough that you'll benefit from wearing compression socks.
Wear compression socks during and after exercise
In conclusion, wearing tights after exercise is an effective way to reduce DOMS and accelerate muscle recovery
Regardless of the sport/exercise, athletes will benefit from wearing compression socks during training, once done, since almost all physical activity is either endurance or strength based, unless you are a leisurely exerciser.
However, in some activities, such as a marathon, it is very important to wear compression socks during and after the race.
High-intensity, prolonged activities, such as marathon running, are known to increase the risk of transient activation of blood clotting (clotting), platelet aggregation, and fibrinolytic activity. Medically speaking, your blood becomes more "clumped," which is why 1 in 1,000 endurance runners will develop a blood clot after a workout.

Causes of blood clots in marathon and distance runners?
-
Dehydration - thickens your blood.
-
Travel - Many marathon runners and triathletes travel long distances to compete. Sitting in a car, train, bus or plane for more than 4 hours doubles your chances of blood clotting.
-
Repetitive Microtrauma - When you cut yourself, your blood cells (platelets) combine at the cut and form a clot to stop the bleeding. After 26+ miles of runs and 20,000 steps, your muscles are undergoing micro-tears, which are like little decoupages inside your muscles, where your body increases the consistency or clotting effect of the blood in an attempt to heal the muscle damage.
-
Thicker blood - Endurance athletes train with more oxygen in their blood than most people, which is good for performance. However, these extra red blood cells can thicken your blood.
-
Endothelial (artery) damage - During exercise, the heart pumps out more blood with each beat than it does at rest. This can lead to increased pressure that can cause damage to your arteries, especially over 26.2 miles, while driving as fast as possible.
-
Those who wore knee-length compression stockings had about a 30 percent reduction in tests of blood clot-inducing enzymes, according to the marathon runners' blood levels.
Running a marathon can upset your coagulation and fibrinolysis balance, the balance between too much blood clotting and no blood clotting at all. Wearing compression stockings maintains this balance by increasing blood flow and circulation, speeding up the rate of blood purification, detoxification, and reoxygenation.
How Long Should You Wear Compression Socks?
Wearing socks for only 1 or 2 hours is not enough to provide significant benefits. After completing the activity, your goal should be to wear socks for 6+ hours. If you've just completed a marathon or long-distance workout, you'll want to wear socks for 6 to 12 hours a day, and continue to wear them for the next few days after your intense workout.
In studies that didn't show positive results, users didn't wear socks long enough to get any benefit. Since socks speed up blood flow, just adding a few hours to your circulation isn't enough to make a difference, especially considering that super-intensive workouts can make your pain linger for 4 or 5 days.
Also, keep in mind that you may want to switch to a new pair of compression socks after an activity or workout. As you can see from the graph below, there are a number of complex factors at play when wearing compression socks outdoors, all of which affect the degree of compression.
Compression Socks: Travel and Sports Performance
Jet lag is often associated with individuals rapidly traversing three or more meridian time zones; however, it has also been suggested that performance degradation occurs when traversing two time zones.
Flight, jet lag and performance
Athletes are at higher risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism and jet lag while flying after intense training or competition.
-
limited space
-
crowded seating arrangement
-
minimal body movement
-
Low-pressure hypoxic environment (low oxygen)
"Jet lag," or circadian rhythm disturbance, manifests as a general feeling of tiredness, disrupted sleep, poor concentration and motivation, and/or decreased mental and physical performance, and persists until resynchronization with the new environment.
Disrupt your normal circadian rhythm with just a 2-hour plane trip.
Participants in the current study who wore pressure suits felt less tired and sore while traveling
A 2019 Australian study looked at the effects of an 8-hour flight and compression stockings in elite women's volleyball players. The team concluded that "exercise compression socks maintain athletic performance and reduce lower extremity swelling when worn in flight". The researchers also noted that "this also coincided with improved subjective scores of alertness, fatigue, muscle soreness, and overall fitness among participants who wore compression stockings."
A general rule of thumb is that it takes a day of recovery to cross a time zone. However, when wearing compression stockings, recovery time is accelerated by 1/2 day or 50% due to improved resting circulation, which leads to increased oxygen in the muscles, improved muscle repair from restricted pressure configurations, and improved first night sleep at your new destination.
Summarize
If you are an endurance athlete, weightlifter, or involved in HIIT activities, you will benefit from wearing compression socks during and after. For everyone else, if you're exercising hard enough to cause lower extremity muscle soreness, wear compression stockings for at least six hours after you're done. Also, for long road trips or flights, wear compression socks regardless of the reason for the trip.